# 第4章 预处理器
# loader
工程中除了js,其他资源HTML、CSS、模板、图片、字体,webpack如何处理。
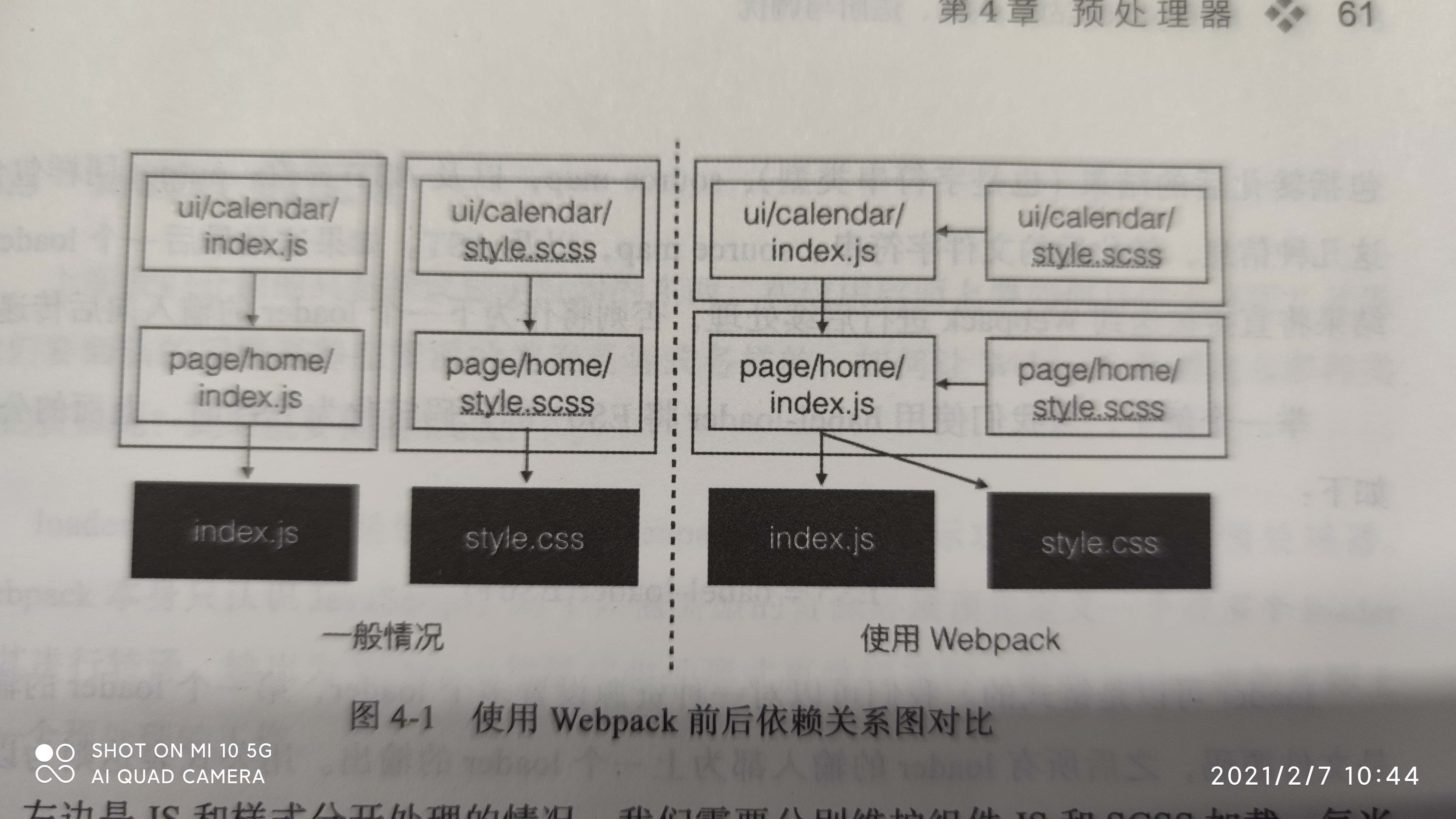
左边是JS和样式分开处理的情况,需要分别维护组件JS和SCSS加载,添加或删除一个组件时都需要进行两次操作:引入js、引入SCSS或者删除。
右边是使用Webpack将SCSS通过JS来引入的情况。当移除这个组件时,只需要移除对于组件JS的引用即可。
# loader概述
每个loader本质上都是一个函数。函数的输入和输出都必须是字符串、抽象语法树(AST)。
output = loaderA(loaderB(loaderC(input)));
Webpack本身只认识js,对于其他类型的资源必须预先定义一个或多个loader对其进行转译,输出为webpack能够接收的形式再继续进行。
webpack本身并不包含任何loader,需要从npm下载:
npm i css-loader
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [{
test: /\.css/,
use: ['style-loader', 'css-loader']
}]
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
webpack打包是是按照数组从后往前的顺序将资源交给loader处理的,因此最后生效的放在前面。css-loader作用是处理css的各种加载语法(@import和url()函数等),如果要使样式起作用还需要style-loader来把样式插入页面。
# options
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [{
test: /\.css/,
use: ['style-loader', {
loader: 'css-loader',
options: {
// css-loader配置项
},
include: /node_modules\/awesome-ui/,
exclude: /node_modules/
}]
}]
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
exclude和include同时存在时,exclude的优先级更高。
# resource和issuer
resource与issuer可用于更加精确的确定模块规则的作用范围。
resource是加载模块,issure是加载者。
rules: [
{
use: ['style-loader', 'css-loader'],
resource: {
test: /\.css$/,
exclude: /node_modules/
},
issuer: {// 只有/src/pages/目录下的js引用css文件,才会生效,否则不会生效。
test: /\.js$/,
include: /src/pages/
}
}
]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# enforce
enforce用来指定一个loader的种类,只接收’pre‘或’post‘两种字符串类型的值。
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [{
test: /\.css/,
enforce: 'pre',
use: ['eslint-loader']
}]
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
上面代码代表它将在所有正常loader之前执行。如果某一个loader需要在所有loader之后执行,则配置enforce为post。
不使用enforce而只要保证loader顺序是正确的即可,enforce主要目的是使模块规则更加清晰。
# 常用loader介绍
# babel-loader
babel-loader用来处理ES6+并将其编译为ES5,它使我们可以在项目中使用最新的语言特性,同时不必特别关注这些特性在不同平台的兼容问题。
npm i babel-loader @babel/core @babel/preset-env
babel-loader: 是babel与webpack协同工作的模块。
@babel/core: 是babel编译器的核心模块。
@babel/preset-env: 是babel推荐的预置器,可根据用户设置的目标环境自动添加所需要的插件和补丁来编译es6+代码。
rule:[
{
test: /\.js$/,
exclude: /node_modules/,
use: {
loader: 'babel-loader',
options: {
cacheDirectory: true,
presets: [[
'env',
{modules: false}
]]
}
}
}
]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
cacheDirectory为true会启用缓存机制,在重复打包未改变过的模块时防止二次编译,同时也会加快打包速度。cacheDirectory可以接收一个字符串类型的路径来作为缓存路径,这个值也可以为true,此时其缓存的路径指向node_modules/.cache/babel-loader
@babel/preset-env会将ES6 Module转化为CommonJS的形式,这会导致Webpack中的tree-shaking特性失效。将@babel/preset-env的module配置项设置为false会禁用模块语句的转化,而将ES6 Module的语法交给webpack处理。
babel-loader支持从.babelrc文件读取babel配置,因此可以将presets和plugins从webpack配置文件中提取出来,也能达到相同的效果。
# ts-loader
用于连接Typescript和Webpack的模块。
# html-loader
用于将HTML文件转化为字符串并进行格式化,这使得我们可以把一段HTML片段通过JS加载进来。
npm i html-loader
rule: [
{
test: /\.html$/,
use: 'html-loader'
}
]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# file-loader
file-loader用于打包文件类型的资源,并返回其publicPath。
rules: [
{
test: /\.(png|jpg|gif)$/,
use: 'file-loader'
}
]
2
3
4
5
6
output.path是资源打包后输出路径。output.publicPath是资源引用路径。由于配置中没指定output.publicPath,因此打印出的图片路径只是文件名。默认为hash值加上文件后缀。
// 配置output.publicPath为'./assets/'后
import img from './avatar.jpg'
console.log(img);// ./assets/c679879879087897976.jpg
2
3
use: {
loader: 'file-loader',
options: {
name: '[name].[ext]',
publicPath: './another-path/'
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
file-loader也可以在options中设置publicPath,会直接覆盖output.publicPath。
# url-loader
url-loader与file-loader唯一不同的是,可以设置一个文件大小的值,当大于该值时与file-loader一样返回publicPath,而小于该值时返回文件base64形式编码。
use: {
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
limit: 10240,
name: '[name]-[ext]',
publicPath: './path/'
}
}
import img from './img.jpg';
console.log(img); // data:image/jpeg:base64,/9dkkdjs....
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# vue-loader
vue-loader可以将组件的模板、js、样式进行拆分。
npm i vue-loader vue vue-template-compiler css-loader
rules: [
{
test: /\.vue$/,
use: 'vue-loader'
}
]
2
3
4
5
6
# 自定义loader
# 为所有js启用严格模式
// force-strict-loader
module.exports = function (content) {
var pre = '\'use strict\';\n\n';
return pre + content;
}
// webpack
module: {
rule: [
{
test: /\.js$/,
use: 'force-strict-loader'
}
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 启用缓存
当文件输入和其依赖没有发生变化时,应该让loader直接使用缓存,而不是重复进行转换工作。webpack中可以使用this.cacheable进行控制。
// force-strict-loader
module.exports = function (content) {
if(this.cacheable) {
this.cacheable();
}
var pre = '\'use strict\';\n\n';
return pre + content;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 获取options
module: {
rule: [
{
test: /\.js$/,
use: {
loader: 'force-strict-loader',
options: {
sourceMap: true
}
}
}
]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
首先需要:
npm i loader-utils
// force-strict-loader
var loaderUtils = require('loader-utils');
module.exports = function (content) {
if(this.cacheable) {
this.cacheable();
}
// 获取和打印options
var options = loaderUtils.getOptions(this) || {};
console.log(options);
var pre = '\'use strict\';\n\n';
return pre + content;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# source-map
source-map可以便于开发者在浏览器控制台查看源码。
var loaderUtils = require('loader-utils');
var SourceNode = require('source-map').SourceNode;
var SourceMapConsumer = require('source-map').SourceMapConsumer;
module.exports = function(content, sourceMap) {
var options = loaderUtils.getOptions(this) || {}
if(options.sourceMap && sourceMap) { // sourceMap是上一个loader传递下来的
var currentRequest = loaderUtils.getCurrentRequest(this)
var node = SourceNode.fromStringWithSourceMap(
content,
new SourceMapConsumer(sourceMap)
)
node.prepend(pre);
var result = node.toStringWithSourceMap({file: currentRequest});
var callback = this.async();
callback(null, result.code, result.map.toJSON());
}
// 不支持source-map
return pre + content;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
← 第3章 资源输入输出 第5章 样式处理 →